Home » Solar Energy
 Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) systems use very different technology than photovoltaic systems. CSP systems use the sun as the "thermal heat" source as opposed to the photon energy of the sun as PV systems do. Most electric power plants use some form of fossil fuel as the thermal heat source to boil water into steam. The steam then spins a large turbine, which drives a generator to produce electricity.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) systems use very different technology than photovoltaic systems. CSP systems use the sun as the "thermal heat" source as opposed to the photon energy of the sun as PV systems do. Most electric power plants use some form of fossil fuel as the thermal heat source to boil water into steam. The steam then spins a large turbine, which drives a generator to produce electricity.
Solar activity refers to a series of complex phenomena in the solar atmosphere, including sunspots, flares, prominences, coronal transient events, etc. These activities are usually caused by electromagnetic processes in the solar atmosphere. During periods of intense solar activity, the sun will radiate large amounts of ultraviolet rays, Phenomena such as ionospheric disturbances, and even the increase or decrease in the number of sunspots can affect the Earth's climate. Therefore, research on solar activity is of extremely important significance for humans to understand the universe, monitor the space environment, develop science and technology, and prevent natural disasters.
These activities are usually caused by electromagnetic processes in the solar atmosphere. During periods of intense solar activity, the sun will radiate large amounts of ultraviolet rays, Phenomena such as ionospheric disturbances, and even the increase or decrease in the number of sunspots can affect the Earth's climate. Therefore, research on solar activity is of extremely important significance for humans to understand the universe, monitor the space environment, develop science and technology, and prevent natural disasters.
 These activities are usually caused by electromagnetic processes in the solar atmosphere. During periods of intense solar activity, the sun will radiate large amounts of ultraviolet rays, Phenomena such as ionospheric disturbances, and even the increase or decrease in the number of sunspots can affect the Earth's climate. Therefore, research on solar activity is of extremely important significance for humans to understand the universe, monitor the space environment, develop science and technology, and prevent natural disasters.
These activities are usually caused by electromagnetic processes in the solar atmosphere. During periods of intense solar activity, the sun will radiate large amounts of ultraviolet rays, Phenomena such as ionospheric disturbances, and even the increase or decrease in the number of sunspots can affect the Earth's climate. Therefore, research on solar activity is of extremely important significance for humans to understand the universe, monitor the space environment, develop science and technology, and prevent natural disasters.
 According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), located in Golden Colorado and Washington DC, the average residential household in the U.S. installs a 5-kWh system and during 2017, it cost on average $2.80 per DC watt or $14,000 (5000 times $2.80) before incentives. Utilities on the other hand typically install systems in the 100 mega-watt or greater range. The average installed "fixed" solar panel system cost during 2017 was $1.03 per watt.
According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), located in Golden Colorado and Washington DC, the average residential household in the U.S. installs a 5-kWh system and during 2017, it cost on average $2.80 per DC watt or $14,000 (5000 times $2.80) before incentives. Utilities on the other hand typically install systems in the 100 mega-watt or greater range. The average installed "fixed" solar panel system cost during 2017 was $1.03 per watt.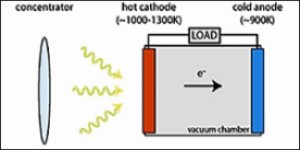 The concept of the Shockley Queisser Efficiency Limit was first formulated by William Shockley and Hans Queisser in1961. It represents the maximum efficiency that any single-junction solar cellcan achieve, typically around 33% under standard test conditions (STC). Theseconditions simulate solar noon during the spring and autumn equinoxes in thecontinental United States, with the solar cell directly facing the sun.
The concept of the Shockley Queisser Efficiency Limit was first formulated by William Shockley and Hans Queisser in1961. It represents the maximum efficiency that any single-junction solar cellcan achieve, typically around 33% under standard test conditions (STC). Theseconditions simulate solar noon during the spring and autumn equinoxes in thecontinental United States, with the solar cell directly facing the sun.
The main way the sun releases energy is through nuclear fusion reactions. The sun's nuclear reaction zone is undergoing a large amount of hydrogen nuclear fusion every second, releasing huge amounts of light and heat energy.  This process has been going on for about 4.6 billion years, making the sun the primary energy source for Earth and the other planets in the solar system. Solar flares are the most intense form of energy release in the solar system. They consist of a violent release of energy on the surface of the sun. Although solar activity is frequent and intense, the specific time and intensity of its outbreak are still difficult to predict. Scientists recommend continuous monitoring of solar activity, to better understand the internal mechanisms and magnetic field changes of the sun.
This process has been going on for about 4.6 billion years, making the sun the primary energy source for Earth and the other planets in the solar system. Solar flares are the most intense form of energy release in the solar system. They consist of a violent release of energy on the surface of the sun. Although solar activity is frequent and intense, the specific time and intensity of its outbreak are still difficult to predict. Scientists recommend continuous monitoring of solar activity, to better understand the internal mechanisms and magnetic field changes of the sun.
 This process has been going on for about 4.6 billion years, making the sun the primary energy source for Earth and the other planets in the solar system. Solar flares are the most intense form of energy release in the solar system. They consist of a violent release of energy on the surface of the sun. Although solar activity is frequent and intense, the specific time and intensity of its outbreak are still difficult to predict. Scientists recommend continuous monitoring of solar activity, to better understand the internal mechanisms and magnetic field changes of the sun.
This process has been going on for about 4.6 billion years, making the sun the primary energy source for Earth and the other planets in the solar system. Solar flares are the most intense form of energy release in the solar system. They consist of a violent release of energy on the surface of the sun. Although solar activity is frequent and intense, the specific time and intensity of its outbreak are still difficult to predict. Scientists recommend continuous monitoring of solar activity, to better understand the internal mechanisms and magnetic field changes of the sun.
Solar energy refers to the thermal radiation energy of the sun, which uses sunlight to convert energy into usable forms, such as electricity and heat.  In a broad sense, solar energy also includes wind energy, chemical energy, water energy, etc. Solar energy is a clean and renewable energy source. Since the birth of life on Earth, it has mainly relied on the thermal radiation energy provided by the sun to survive. Especially now that fossil fuels are dwindling, solar energy has become an important source of energy for human beings, and continues to develop. The utilization of solar energy is mainly through two methods: photothermal conversion and photoelectric conversion. Solar power generation is an emerging renewable energy source.
In a broad sense, solar energy also includes wind energy, chemical energy, water energy, etc. Solar energy is a clean and renewable energy source. Since the birth of life on Earth, it has mainly relied on the thermal radiation energy provided by the sun to survive. Especially now that fossil fuels are dwindling, solar energy has become an important source of energy for human beings, and continues to develop. The utilization of solar energy is mainly through two methods: photothermal conversion and photoelectric conversion. Solar power generation is an emerging renewable energy source.
 In a broad sense, solar energy also includes wind energy, chemical energy, water energy, etc. Solar energy is a clean and renewable energy source. Since the birth of life on Earth, it has mainly relied on the thermal radiation energy provided by the sun to survive. Especially now that fossil fuels are dwindling, solar energy has become an important source of energy for human beings, and continues to develop. The utilization of solar energy is mainly through two methods: photothermal conversion and photoelectric conversion. Solar power generation is an emerging renewable energy source.
In a broad sense, solar energy also includes wind energy, chemical energy, water energy, etc. Solar energy is a clean and renewable energy source. Since the birth of life on Earth, it has mainly relied on the thermal radiation energy provided by the sun to survive. Especially now that fossil fuels are dwindling, solar energy has become an important source of energy for human beings, and continues to develop. The utilization of solar energy is mainly through two methods: photothermal conversion and photoelectric conversion. Solar power generation is an emerging renewable energy source.
 Solar energy's development commenced in 1839 when French physicist Alexander Edmond Becquerel (1820-1891) conducted research that led to the discovery of the "photovoltaic (PV) effect." While experimenting with a solid electrode in an electrolyte solution at the age of 19 in his father's laboratory, Becquerel observed the development of voltage when light struck the electrode. This phenomenon, later termed the Becquerel Effect, marked the foundational understanding of solar energy conversion.
Solar energy's development commenced in 1839 when French physicist Alexander Edmond Becquerel (1820-1891) conducted research that led to the discovery of the "photovoltaic (PV) effect." While experimenting with a solid electrode in an electrolyte solution at the age of 19 in his father's laboratory, Becquerel observed the development of voltage when light struck the electrode. This phenomenon, later termed the Becquerel Effect, marked the foundational understanding of solar energy conversion.

Category
Featured Articles
Expanding Research on Solar Energy ...
The application fields of solar energy are very wide, covering many fields such as the photonic industry, new energy photothermal ...
Exploring Concentrated Solar Power ...
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) systems use very different technology than photovoltaic systems. CSP systems use the sun as the ...
Solar Cell Manufacturing Process
Solar cells are made of various materials, the most common of which include silicon, indium gallium, cadmium selenide, etc. These ...
The Evolution of Grid Electricity ...
"Electricity" cannot be stored on the grid; generation must be approximately equal to consumption at all times. However, ...
Solar Activity: Sunspots, Magnetism & ...
Solar activity refers to a series of complex phenomena in the solar atmosphere, including sunspots, flares, prominences, coronal ...
