Home » Solar Basics
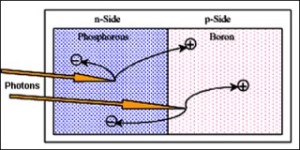 A p/n junction is formed when two types of semiconductors, n-type (excess electrons) and p-type (excess holes), come into contact. The term p/n junction refers to the joint interface and the immediate surrounding area of the two semiconductors. If the joint is made by two separate semiconductor crystals, this is a rough interface known as a grain boundary. A grain boundary has different electrical properties than a single crystalline interface. P/N junctions are normally created in a single crystal of semiconductor by doping each side with different "dopants". The discovery of the p/n junction is usually attributed to American physicist Russell Ohl of Bell Laboratories.
A p/n junction is formed when two types of semiconductors, n-type (excess electrons) and p-type (excess holes), come into contact. The term p/n junction refers to the joint interface and the immediate surrounding area of the two semiconductors. If the joint is made by two separate semiconductor crystals, this is a rough interface known as a grain boundary. A grain boundary has different electrical properties than a single crystalline interface. P/N junctions are normally created in a single crystal of semiconductor by doping each side with different "dopants". The discovery of the p/n junction is usually attributed to American physicist Russell Ohl of Bell Laboratories.
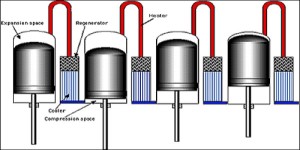 The original Stirling engine was developed in 1816 by Robert Stirling as an alternative to the early steam engine which tended to explode. However, its practical use was confined to low power domestic applications. The Stirling engine is noted for its high efficiency (up to 40%), quiet operation, and the ease with which it can use almost any heat source, in this case the sun's heat. This compatibility with renewable energy has become significant because of concerns for the US addiction to oil, the carbon footprint, and climate change consequences. The Stirling engine is a waterless CSP technology.
The original Stirling engine was developed in 1816 by Robert Stirling as an alternative to the early steam engine which tended to explode. However, its practical use was confined to low power domestic applications. The Stirling engine is noted for its high efficiency (up to 40%), quiet operation, and the ease with which it can use almost any heat source, in this case the sun's heat. This compatibility with renewable energy has become significant because of concerns for the US addiction to oil, the carbon footprint, and climate change consequences. The Stirling engine is a waterless CSP technology.
The solar inverter is the core component of the solar photovoltaic system. When sunlight hits the solar panels, the power generated by these panels can only be direct current, and what we need is alternating current, because most electrical equipment uses Alternating current, at this time, the role of the solar inverter becomes apparent. Its main function is to convert DC power generated by solar panels into AC power for domestic, industrial or commercial use, or for feedback into the grid. The design of the inverter must be efficient and reliable to ensure the stability and economy of the solar system. In modern photovoltaic systems, the inverter is not only an energy conversion device, but also often has a communication interface that can be connected to the smart grid system to achieve remote monitoring and management. Through these functions, the inverter facilitates the interaction between the photovoltaic power generation system and the power grid, increasing the intelligence and automation level of the system.
Its main function is to convert DC power generated by solar panels into AC power for domestic, industrial or commercial use, or for feedback into the grid. The design of the inverter must be efficient and reliable to ensure the stability and economy of the solar system. In modern photovoltaic systems, the inverter is not only an energy conversion device, but also often has a communication interface that can be connected to the smart grid system to achieve remote monitoring and management. Through these functions, the inverter facilitates the interaction between the photovoltaic power generation system and the power grid, increasing the intelligence and automation level of the system.
 Its main function is to convert DC power generated by solar panels into AC power for domestic, industrial or commercial use, or for feedback into the grid. The design of the inverter must be efficient and reliable to ensure the stability and economy of the solar system. In modern photovoltaic systems, the inverter is not only an energy conversion device, but also often has a communication interface that can be connected to the smart grid system to achieve remote monitoring and management. Through these functions, the inverter facilitates the interaction between the photovoltaic power generation system and the power grid, increasing the intelligence and automation level of the system.
Its main function is to convert DC power generated by solar panels into AC power for domestic, industrial or commercial use, or for feedback into the grid. The design of the inverter must be efficient and reliable to ensure the stability and economy of the solar system. In modern photovoltaic systems, the inverter is not only an energy conversion device, but also often has a communication interface that can be connected to the smart grid system to achieve remote monitoring and management. Through these functions, the inverter facilitates the interaction between the photovoltaic power generation system and the power grid, increasing the intelligence and automation level of the system.
The sun produces an unbelievable amount of energy that reaches the earth. The amount of energy that is absorbed by the earth in one hour is more energy than mankind uses in one year.  The total amount of solar energy reaching the earth in one year is huge - twice as much energy as ever existed from all sources of coal, oil, natural gas, and uranium combined. The amount of solar energy that reaches any given location varies by latitude, time of year, time of day, and local weather. The theoretical basis of solar cells and solar panels is based on the photoelectric effect, that is, when sunlight shines on a specific semiconductor material, the electrons in the material will be excited and generate an electric current. This effect is the basis for converting solar energy into electrical energy.
The total amount of solar energy reaching the earth in one year is huge - twice as much energy as ever existed from all sources of coal, oil, natural gas, and uranium combined. The amount of solar energy that reaches any given location varies by latitude, time of year, time of day, and local weather. The theoretical basis of solar cells and solar panels is based on the photoelectric effect, that is, when sunlight shines on a specific semiconductor material, the electrons in the material will be excited and generate an electric current. This effect is the basis for converting solar energy into electrical energy.
 The total amount of solar energy reaching the earth in one year is huge - twice as much energy as ever existed from all sources of coal, oil, natural gas, and uranium combined. The amount of solar energy that reaches any given location varies by latitude, time of year, time of day, and local weather. The theoretical basis of solar cells and solar panels is based on the photoelectric effect, that is, when sunlight shines on a specific semiconductor material, the electrons in the material will be excited and generate an electric current. This effect is the basis for converting solar energy into electrical energy.
The total amount of solar energy reaching the earth in one year is huge - twice as much energy as ever existed from all sources of coal, oil, natural gas, and uranium combined. The amount of solar energy that reaches any given location varies by latitude, time of year, time of day, and local weather. The theoretical basis of solar cells and solar panels is based on the photoelectric effect, that is, when sunlight shines on a specific semiconductor material, the electrons in the material will be excited and generate an electric current. This effect is the basis for converting solar energy into electrical energy.
Solar cells are made of various materials, the most common of which include silicon, indium gallium, cadmium selenide, etc. These materials play a vital role in the manufacturing process of solar cells. Silicon is one of the most commonly used solar cell materials at present. It has good semiconductor properties, can generate electron-hole pairs under light and convert them into electrical energy,  and has high photoelectric conversion efficiency and stability. Currently, the main types of solar cells include silicon crystal solar cells, thin film solar cells, and some emerging solar cells. The manufacturing processes of various solar cells are constantly being optimized and innovated to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the stability and durability of the cells. With the advancement of science and technology, new manufacturing technologies and materials may emerge in the future, promoting further innovation in solar cell technology.
and has high photoelectric conversion efficiency and stability. Currently, the main types of solar cells include silicon crystal solar cells, thin film solar cells, and some emerging solar cells. The manufacturing processes of various solar cells are constantly being optimized and innovated to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the stability and durability of the cells. With the advancement of science and technology, new manufacturing technologies and materials may emerge in the future, promoting further innovation in solar cell technology.
 and has high photoelectric conversion efficiency and stability. Currently, the main types of solar cells include silicon crystal solar cells, thin film solar cells, and some emerging solar cells. The manufacturing processes of various solar cells are constantly being optimized and innovated to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the stability and durability of the cells. With the advancement of science and technology, new manufacturing technologies and materials may emerge in the future, promoting further innovation in solar cell technology.
and has high photoelectric conversion efficiency and stability. Currently, the main types of solar cells include silicon crystal solar cells, thin film solar cells, and some emerging solar cells. The manufacturing processes of various solar cells are constantly being optimized and innovated to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the stability and durability of the cells. With the advancement of science and technology, new manufacturing technologies and materials may emerge in the future, promoting further innovation in solar cell technology.
 "Electricity" cannot be stored on the grid; generation must be approximately equal to consumption at all times. However, "energy" can be stored although losses are incurred in the process. At the moment, there are three proven methods of storing electric energy on the scale of the grid - batteries, molten salt and compressed air. There are also a few new technologies on the horizon. Let us take a look at proven as well as some new technologies.
"Electricity" cannot be stored on the grid; generation must be approximately equal to consumption at all times. However, "energy" can be stored although losses are incurred in the process. At the moment, there are three proven methods of storing electric energy on the scale of the grid - batteries, molten salt and compressed air. There are also a few new technologies on the horizon. Let us take a look at proven as well as some new technologies. The sun periodically emits a prominence on its surface, a distinctive looking figure that is in its outer atmosphere, the Corona, and many times has a swirl or loop configuration. A prominence is a mass of plasma gases and charged particles that are cooler (60,000 degrees C) than their surroundings (a million degrees C). A typical prominence is a billion tons or more of these gases supported by huge magnetic forces.
The sun periodically emits a prominence on its surface, a distinctive looking figure that is in its outer atmosphere, the Corona, and many times has a swirl or loop configuration. A prominence is a mass of plasma gases and charged particles that are cooler (60,000 degrees C) than their surroundings (a million degrees C). A typical prominence is a billion tons or more of these gases supported by huge magnetic forces.

Category
Featured Articles
Expanding Research on Solar Energy ...
The application fields of solar energy are very wide, covering many fields such as the photonic industry, new energy photothermal ...
Exploring Concentrated Solar Power ...
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) systems use very different technology than photovoltaic systems. CSP systems use the sun as the ...
Solar Cell Manufacturing Process
Solar cells are made of various materials, the most common of which include silicon, indium gallium, cadmium selenide, etc. These ...
The Evolution of Grid Electricity ...
"Electricity" cannot be stored on the grid; generation must be approximately equal to consumption at all times. However, ...
Solar Activity: Sunspots, Magnetism & ...
Solar activity refers to a series of complex phenomena in the solar atmosphere, including sunspots, flares, prominences, coronal ...
